medulla
Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
Related to medulla: adrenal medulla
me·dul·la
(mĭ-dŭl′ə)n. pl. me·dul·las or me·dul·lae (-dŭl′ē)
1. The inner core of certain organs or body structures, such as the marrow of bone.
2. The medulla oblongata.
3. See myelin.
4. Botany
a. The pith in the stems or roots of certain plants.
b. The central portion of a thallus in certain lichens and red or brown algae.
[Middle English, from Latin, perhaps alteration (influenced by medius, middle) of *merulla.]
me·dul′lar, med′ul·lar′y (mĕd′l-ĕr′ē, mə-dŭl′ə-rē) adj.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
medulla
(mɪˈdʌlə)n, pl -las or -lae (-liː)
1. (Anatomy) anatomy
a. the innermost part of an organ or structure
b. short for medulla oblongata
2. (Botany) botany another name for pith4
[C17: from Latin: marrow, pith, probably from medius middle]
meˈdullary, meˈdullar adj
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
me•dul•la
(məˈdʌl ə)n., pl. -dul•las, -dul•lae (-ˈdʌl i)
1.
a. the marrow of the bones.
b. the soft marrowlike center of an organ, as the kidney or adrenal gland.
2. the pith of plants.
[1635–45; < Latin: marrow, pith]
med•ul•lar•y (ˈmɛd lˌɛr i, ˈmɛdʒ əˌlɛr i, məˈdʌl ə ri) adj.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
me·dul·la
(mĭ-dŭl′ə, mĭ-do͞o′lə)1. See medulla oblongata.
2. The central core of an anatomical structure, such as the adrenal gland or the kidney.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
medulla
The inner part of some organs, including the kidneys; a name for bone marrow.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
Switch to new thesaurus
| Noun | 1. | 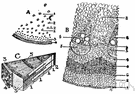 medulla - a white fatty substance that forms a medullary sheath around the axis cylinder of some nerve fibers medulla - a white fatty substance that forms a medullary sheath around the axis cylinder of some nerve fibersmedullary sheath, myelin sheath - a layer of myelin encasing (and insulating) the axons of medullated nerve fibers fat - a soft greasy substance occurring in organic tissue and consisting of a mixture of lipids (mostly triglycerides); "pizza has too much fat" |
| 2. | 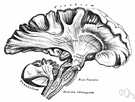 medulla - lower or hindmost part of the brain; continuous with spinal cord; (`bulb' is an old term for medulla oblongata); "the medulla oblongata is the most vital part of the brain because it contains centers controlling breathing and heart functioning" medulla - lower or hindmost part of the brain; continuous with spinal cord; (`bulb' is an old term for medulla oblongata); "the medulla oblongata is the most vital part of the brain because it contains centers controlling breathing and heart functioning"neural structure - a structure that is part of the nervous system brain stem, brainstem, brain-stem - the part of the brain continuous with the spinal cord and comprising the medulla oblongata and pons and midbrain and parts of the hypothalamus respiratory center - the center in the medulla oblongata and pons that integrates sensory information about the level of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood and determines the signals to be sent to the respiratory muscles | |
| 3. | medulla - the inner part of an organ or structure in plant or animal animal tissue - the tissue in the bodies of animals adrenal medulla - the medulla of the adrenal gland; secretes epinephrine plant tissue - the tissue of a plant cortex - the tissue forming the outer layer of an organ or structure in plant or animal |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
TranslationsSelect a language:
Spanish / Español
Collins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
me·dul·la
n. médula, pop. tuétano, parte interna o central de un órgano;
___ oblongata → ___ oblongata, bulbo raquídeo, porción de la médula localizada en la base del cráneo;
___ ossium, bone marrow → ___ ósea.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
medulla
n (pl -lae) (of the brainstem) bulbo raquídeo, médula oblonga; adrenal — médula suprarrenal or adrenalEnglish-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.