hormone
(redirected from hormonic)Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia.
Related to hormonic: harmonic series, harmonic analysis, Harmonic sequence, Harmonic function, harmonic scalpel
hor·mone
(hôr′mōn′)n.
1.
a. A substance, usually a peptide or steroid, produced by one tissue and conveyed by the bloodstream to another to effect physiological activity, such as growth or metabolism.
b. A synthetic compound that acts like a hormone in the body.
2. Any of various similar substances found in plants and insects that regulate development.
[From Greek hormōn, present participle of hormān, to urge on, from hormē, impulse; see er- in Indo-European roots.]
hor·mon′al (-mō′nəl), hor·mon′ic (-mŏn′ĭk) adj.
hor·mon′al·ly adv.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
hormone
(ˈhɔːməʊn)n
1. (Biochemistry) a chemical substance produced in an endocrine gland and transported in the blood to a certain tissue, on which it exerts a specific effect
2. (Biochemistry) an organic compound produced by a plant that is essential for growth
3. (Biochemistry) any synthetic substance having the same effects
[C20: from Greek hormōn, from horman to stir up, urge on, from hormē impulse, assault]
horˈmonal, hormonic adj
horˈmonally adv
ˈhormoneˌlike adj
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
hor•mone
(ˈhɔr moʊn)n.
1. any of various internally secreted compounds formed in endocrine glands that affect the functions of specifically receptive organs or tissues when transported to them by the body fluids.
2. a synthetic substance that acts like such a compound when introduced into the body.
3. any of various plant compounds, as auxin or gibberellin, that control growth and differentiation of plant tissue.
[1900–05; < Greek hormôn, present participle of hormân to set in motion, stimulate, derivative of hormḗ impetus, impulse]
hor•mo′nal, hor•mon•ic (-ˈmɒn ɪk, -ˈmoʊ nɪk) adj.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
hor·mone
(hôr′mōn′) A substance produced in one part of the body, especially in an endocrine gland, that has an effect on another part of the body, to which it is usually carried in the bloodstream. Hormones regulate many biological processes, including growth and metabolism.
Did You Know? On the inside, humans are bathing in a sea of hormones, chemical compounds that regulate many essential activities in the body. A lot of hormones are produced in glands known as endocrine glands, such as the thyroid gland, pancreas, and ovaries, and travel from there through the bloodstream before arriving at their target sites of action. Specialized cells of the nervous system also produce hormones. Hormones are not found only in humans, but also in all other animals and plants. The variety of different functions hormones have is astounding. Insulin, secreted by the pancreas, regulates the absorption of sugars in the body. Thyroid hormones regulate the rate of cell metabolism and affect many other processes, including reproduction. Growth hormone, secreted by the pituitary gland, controls growth of the body. Estrogen and testosterone control sexual development. Some of the hormones released in the brain, known as endorphins, act as natural painkillers. When the amounts of these or other hormones are abnormal, disease can result. Too little insulin causes diabetes, too little estrogen weakens the bones of older women, and too much growth hormone causes people to grow without stopping. Fortunately, these diseases can usually be treated, either with hormones made artificially in laboratories or by operating on the affected gland.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
hormone
A chemical messenger that is produced in one part of an organism and acts in another part.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
Switch to new thesaurus
| Noun | 1. | 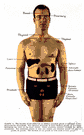 hormone - the secretion of an endocrine gland that is transmitted by the blood to the tissue on which it has a specific effect hormone - the secretion of an endocrine gland that is transmitted by the blood to the tissue on which it has a specific effectsecretion - a functionally specialized substance (especially one that is not a waste) released from a gland or cell ACTH, adrenocorticotrophic hormone, adrenocorticotrophin, adrenocorticotropic hormone, adrenocorticotropin, corticotrophin, corticotropin - a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates the adrenal cortex Adrenalin, adrenaline, epinephrin, epinephrine - a catecholamine secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to stress (trade name Adrenalin); stimulates autonomic nerve action gastrointestinal hormone, GI hormones - hormones that affect gastrointestinal functioning glucagon - a hormone secreted by the pancreas; stimulates increases in blood sugar levels in the blood (thus opposing the action of insulin) gonadotrophic hormone, gonadotrophin, gonadotropic hormone, gonadotropin - hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland and placenta; stimulates the gonads and controls reproductive activity insulin - hormone secreted by the isles of Langerhans in the pancreas; regulates storage of glycogen in the liver and accelerates oxidation of sugar in cells melatonin - hormone secreted by the pineal gland neurohormone - a hormone that is released by nerve impulses (e.g., norepinephrine or vasopressin) oxytocin, Pitocin - hormone secreted by the posterior pituitary gland (trade name Pitocin); stimulates contractions of the uterus and ejection of milk parathormone, parathyroid hormone - hormone synthesized and released into the blood stream by the parathyroid glands; regulates phosphorus and calcium in the body and functions in neuromuscular excitation and blood clotting relaxin - hormone secreted by the corpus luteum during the last days of pregnancy; relaxes the pelvic ligaments and prepares the uterus for labor hypothalamic releasing factor, hypothalamic releasing hormone, releasing factor, releasing hormone, RH - any of several hormones produced in the hypothalamus and carried by a vein to the anterior pituitary gland where they stimulate the release of anterior pituitary hormones; each of these hormones causes the anterior pituitary to secrete a specific hormone growth hormone, human growth hormone, somatotrophic hormone, somatotrophin, somatotropic hormone, somatotropin, STH - a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland; promotes growth in humans thymosin - hormone secreted by the thymus; stimulates immunological activity of lymphoid tissue thyroid hormone - any of several closely related compounds that are produced by the thyroid gland and are active metabolically ADH, antidiuretic hormone, Pitressin, vasopressin - hormone secreted by the posterior pituitary gland (trade name Pitressin) and also by nerve endings in the hypothalamus; affects blood pressure by stimulating capillary muscles and reduces urine flow by affecting reabsorption of water by kidney tubules sex hormone, steroid hormone, steroid - any hormone affecting the development and growth of sex organs adrenosterone - a steroid having androgenic activity; obtained from the cortex of the adrenal gland glucocorticoid - a steroid hormone that is produced by the adrenal cortex of animals; affects functioning of gonads and has anti-inflammatory activity catecholamine - any of a group of chemicals including epinephrine and norepinephrine that are produced in the medulla of the adrenal gland melanocyte-stimulating hormone, MSH - a hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland that controls the degree of pigmentation in melanocytes thyroid-stimulating hormone, thyrotrophic hormone, thyrotrophin, thyrotropic hormone, thyrotropin, TSH - anterior pituitary hormone that stimulates the function of the thyroid gland protirelin, thyrotropin-releasing factor, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, TRF, TRH - hormone released by the hypothalamus that controls the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone from the anterior pituitary |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
hormone
Hormones
adrenaline or epinephrine, adrenocorticotrophic hormone, androsterone, antidiuretic hormone, bursicon, calcitonin, cholecystokinin or pancreozymin, chorionic gonadotrophin, corpus luteum hormone or progesterone, corticosteroid, corticosterone or adrenocorticotrophic hormone, cortisone, deoxycorticosterone, ecdysone, enterogastrone, erythropoietin, florigen, follicle-stimulating hormone, glucagon, gibberellic acid, gastrin, gonadotrophin, growth hormone or somatotrophin, insulin, interstitial-cell-stimulating hormone or luteinizing hormone, juvenile hormone, lactogenic hormone, luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone, luteotrophin or prolactin, noradrenaline, oestradiol, oestriol, oestrone, oxytocin, progesterone, parathyroid hormone, relaxin, secretin, sex hormone, somatomedin, somatostatin, stilboestrol, testosterone, thyroid-stimulating hormone or thyrotropin, thyroxine, trichlorophenoxyacetic acid, triiodothyronine, vasopressinCollins Thesaurus of the English Language – Complete and Unabridged 2nd Edition. 2002 © HarperCollins Publishers 1995, 2002
Translations
هُرمُونهورمون
hormon
hormon
hormoni
hormon
hormon
hormón
ホルモン
호르몬
hormonas
hormons
hormón
hormon
ฮอร์โมน
hóc-môn
hormone
[ˈhɔːməʊn]A. N (Med) → hormona f
B. CPD hormone replacement therapy N → terapia f hormonal sustitutiva
hormone treatment N → tratamiento m de hormonas
hormone treatment N → tratamiento m de hormonas
Collins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
hormone
[ˈhɔːrməʊn] n → hormone f
modif [balance, imbalance, changes, level] → hormonal(e)hormone replacement therapy n → traitement m hormonal substitutif
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
hormone
n → Hormon nt
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
hormone
(ˈhoːməun) noun a substance produced by certain glands of the body, which makes some organ of the body active. Adrenalin is a hormone.
Kernerman English Multilingual Dictionary © 2006-2013 K Dictionaries Ltd.
hormone
→ هُرمُون hormon hormon Hormon ορμόνη hormona hormoni hormone hormon ormone ホルモン 호르몬 hormoon hormon hormon hormona, hormônio гормон hormon ฮอร์โมน hormon hóc-môn 荷尔蒙Multilingual Translator © HarperCollins Publishers 2009
hor·mone
n. hormona, sustancia química natural del cuerpo que produce o estimula la actividad de un órgano;
growth ___ → ___ del crecimiento;
___ therapy → terapia hormonal;
___ receptor → receptor hormonal;
gonadotropin releasing ___ → ___ liberadora de gonadotropina.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
hormone
n hormona; adrenocorticotropic — (ACTH) corticotropina, hormona adrenocorticotrópica (HACT); antidiuretic — vasopresina, hormona antidiurética; bovine growth — hormona de crecimiento bovina; follicle-stimulating — (FSH) hormona folículo estimulante (HFE), folitropina; gonadotropin-releasing — (GnRH) hormona liberadora de gonadotropina(s); (human) growth — (GH) hormona de(l) crecimiento (humana); luteinizing — (LH) hormona luteinizante (HL); parathyroid — (PTH) hormona paratiroidea (HPT); thyroid — hormona tiroidea; thyroid-stimulating — (TSH) hormona estimulante del or de la tiroides, tirotropinaEnglish-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.